Mirrors, wavelength and more
There are (at least) 2 types of spectroscopy mirrors :
- dielectric mirrors
- metal coated mirrors
Thorlabs :
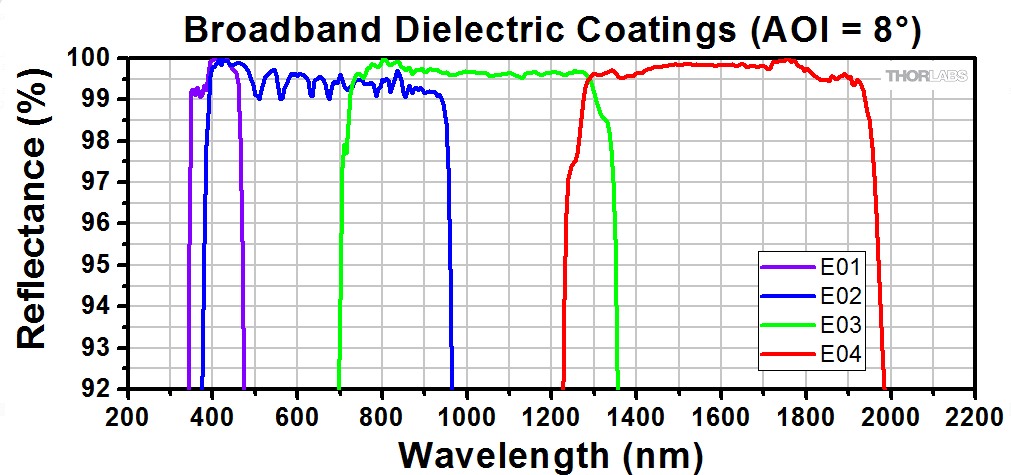
The coating of dielectric mirrors consists of multiple layers of material with different indices of difraction. These layers produce a destructive interference in the forward direction, and hence a constructive interference in the backwards direction : they function as a mirror. It is the same principle as the anti-reflection coating on sun glasses.
The advantage of dielectric mirrors is : high reflection, high damage threshold, more 'scratch' resistant
Disadvantage : reflection is angle dependend, not so broadband as metal coated mirrors, expensive. Not to be used for fs (or ps?) pulses.
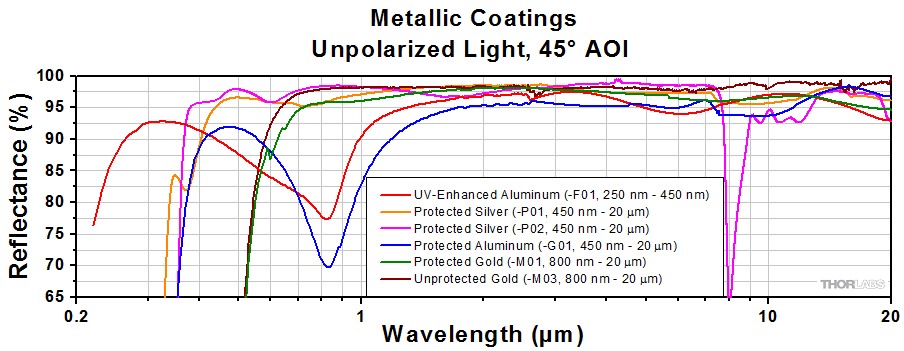
The coating of metal coated mirrors conststs of a thin layer of metal, with optionally a protected layer on top of that.
The layer can be alluminium, silver or gold. Below 400 nm, use alluminium, otherwise silver. Perhaps for the infrared gold might be better.
The unprotected mirrors reflect usually a little better, but are (much) more prone to scratching. Most mirrors are protected.
The advantage of metal coated mirrors is : cheaper then dielectric, more broadband then dielectric. Reflection is only slightly angle dependend. Usable for fs pulses.
Disadvantage : lower reflection then dielectric, lower damage threshold.
The workhorse for our group is : silver protected mirrors -P01.
Use aluminum mirrors for below 400 nm or so (see graph).
Thorlabs price for 1" round mirror
Dielectric E02 : 82 euro
Silver -P01 : 57 euro
Newport
BD1 : Broadband dielectric 1 : VIS 488-694 nm ( 75 euro, cheapest. Depends on substrate)
BD2 : Broadband dielectric 2 : NIR 700-950 nm
